Understanding Display Adapters
HOW DISPLAY ADAPTERS
WORK
Here is a general schematic of a display adapter. Not all
adapters will look like this. This schematic actually represents a PCI card:
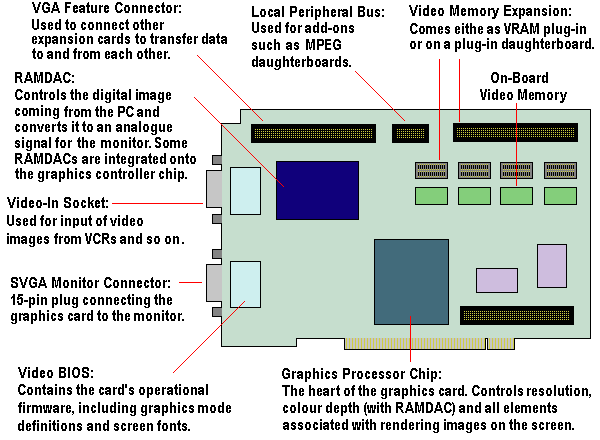
GPU - Graphics Processing Unit
The processor onboard the board which controls all aspects of image rendering.
The gpu executes instructions interpreted by the
adapter's driver.
Frame data is written to the frame buffer ( a memory
space which holds graphics instructions) by the gpu
much faster than by the main system cpu. Thus, since
there's less data congesting the main board bus, the CPU works less.
GPU's are recognized by their heat sinks, and, in
many cases, by their own cooling fans.
Video Memory
All non-integrated display adapters have their own onboard memory. In addition,
higher-end laptops have memory separate from main system RAM, dedicated to AGP
video. There are several different kinds of video memory. Early systems used
conventional DRAM (dynamic ram) which degraded performance because of its high
refresh rate and power requirements.
Shared video memory: On lower end systems, the video is
integrated into the motherboard. The video controller uses a certain amount of
'shared RAM' for video memory. The shared ram (usually 8 mb)
is taken away from main system RAM. Thus, on a 64 Mb system, if the integrated
controller uses '8 Mb shared video RAM', the main system only uses 56 Mb of
RAM, and this is the number you'll see when checking for the memory.
Video RAM (VRAM): Dual-ported Dynamic RAM. Dual porting means
that the memory space can be written to and read from at the same time, unlike
conventional RAM. Video RAM is faster than conventional DRAM.
Windows RAM (WRAM): Not to be associate with the Windows OS.
Dual ported as well, and runs faster than VRAM. Some Matrox
cards use WRAM. Dual ported.
Synchronous Dynamic Ram (SDRAM): Memory and graphics chips
run on a common clock (are synchronized). Thus, SDRAM runs much faster than
Synchronous Graphics Ram (SGRAM): Similar to SDRAM but
faster. Single ported. DDR SGRAM is quite popular.
DRDRAM: The newest type of video memory. It is anticipated
that drdram will be much faster than any current
video memory. Single ported.
RAMDAC
A chip on the motherboard that converts the data in the frame buffer ( the memory space that holds the image), and converts it
into the analogue RGB signal for output to the monitor. DAC means 'digital to
analogue converter'. The RAMDAC reads the contents of the video memory, and
converts it to RGB.
Drivers
Translates the graphics requirements of a system into instructions that are
executed by the display adapter. The driver translates pixel values, line
drawing, shape drawing, etc. A driver's performance can vary depending on
resolution. Some drivers don't perform as well at resolutions
not 'native' to the adapter. This is an effect seen more frequently in
modern laptops.